Thrust-To-Weight Ratio (TWR) Of Jet And Rocket Engines
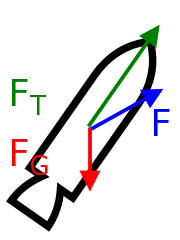
Thrust-to-weight ratio is a dimensionless ratio of thrust to weight of a rocket, jet engine, propeller engine, or a vehicle propelled by such an engine that indicates the performance of the engine or vehicle.
The instantaneous thrust-to-weight ratio of a vehicle varies continually during operation due to progressive consumption of fuel or propellant and in some cases a gravity gradient.
The thrust-to-weight ratio based on initial thrust and weight is often published and used as a figure of merit for quantitative comparison of the initial performance of vehicles.
| Jet Or Rocket Engine | Mass (N) | Thrust (N) | Thrust-To-Weight Ratio (Low To High) |
| RD-0410 nuclear rocket engine | 20,000 | 35,200 | 1.8:1 |
| Pratt & Whitney F119 | 18,000 | 91,000 | 5.1:1 |
| Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 turbojet with reheat (Concorde) | 31,750 | 169,200 | 5.3:1 |
| J58 jet engine (SR-71 Blackbird) | 27,220 | 150,000 | 5.5:1 |
| RD-0750 rocket engine, three-propellant mode | 46,210 | 1,413,000 | 30.6:1 |
| RD-0146 rocket engine | 2,600 | 98,000 | 37.7:1 |
| SSME rocket engine (Space Shuttle) | 31,770 | 2,278,000 | 71.7:1 |
| RD-180 rocket engine | 53,930 | 4,152,000 | 77.0:1 |
| RD-170 rocket engine | 97,500 | 7,887,000 | 80.9:1 |
| F-1 (Saturn V first stage) | 83,910 | 7,740,500 | 92.2:1 |
| NK-33 rocket engine | 12,220 | 1,638,000 | 134.0:1 |
| Merlin 1D rocket engine | 4,400 | 690,000 | 156.8:1 |
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrust-to-weight_ratio



0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home